🤔
Ever found yourself in a debate or an argument?
Of course you have. We all have! Whether it's figuring out who's to blame for the spilled coffee, or
navigating a tricky discussion on social media, arguments are an integral part of human communication.
So, what is Formal Argumentation?
Imagine taking the essence of these everyday disputes and structuring them into a logical framework. This
allows us to analyze, understand, and even predict how arguments unfold! By using rules and structures,
formal argumentation offers a fascinating lens through which we can study the dynamics of decision-making.
The relation of arguments can be evaluated by their stucture or by their relation in a graph form abstracting
their relations.

In asbstract argumentation the arguments are set as nodes and their relations are repesented arrows
arrows (edges). By evaluating the attack and defense relations between the arguments we can derive to a plausible conclusion.
LOUIS: "The spill is entirely John's fault because he's always clumsy and not careful with his movements around the table."
BETTY: "While John might be clumsy, the real issue was the placement of the coffee cup. Louis placed it too close to the edge,
practically setting up for an accident. If it were placed more securely, even a bump wouldn't have caused a spill."
JOHN: "It's true that I bumped into the cup, but the reason I did was that I was startled when Betty suddenly stood up, causing me to turn
quickly and not see the cup. So, it wasn't about being clumsy but an unexpected reaction to Betty's sudden movement."
We can evaluate these arguments and how they "attack" each other and make a conclusions about who to blame about the spilling of the coffee.
Who do you think is to blame for the spilling of the coffee?
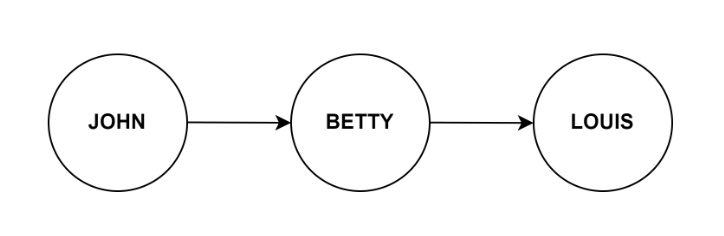
What could be concluded from these frameworks then? There are multiple ways to evaluate each argumentation
situation based on how you look at it. "semantics" and "extensions" serve as the backbone
for understanding and evaluating the complex dance of debate and discussion. Semantics in argumentation theory refers to the rules or principles
that guide us in interpreting which sets of arguments stand strong against criticism and which are not. These sets, known as "extensions," represent groups
of arguments that, when viewed together, are coherent and defend each other against opposing views.
Extensions are essentially the conclusions you draw from
the argumentation framework and depending what rules (semantics) you will draw differing conclusions. We can for example
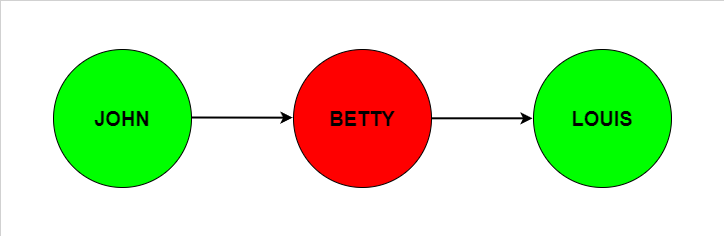
draw the conclusion that we accept (green) John's argument because no other arugment attacks it and therefore reject (red) then Betty's argument because John's accepted attack Betty's argument.
Finally because we have rejected Betty's argument, no argument is now attacking Louis's argument and we can therefore accept (green) it.
But Why Should I Care? Formal argumentation is not just an academic exercise. It's at the heart of artificial intelligence, decision-making systems, and even legal reasoning. By understanding how arguments work, we can develop smarter AI that works with humans as a team and make decisions as we would make them. Within the realm of (symbolic) AI, argumentation approaches are currently considered a promising field of study that can potentially reconcile the need for human control and understanding of AI systems on the one hand and the provision of solid, provable guarantees about system behavior on the other.
Join the Exploration! On this site, you can delve into various argumentation frameworks and conclusions you can draw from them. You can also participate in a survey, helping us to understand how real people "solve" these argumentative puzzles. Your insight is important to us!
No prior knowledge needed. Just bring your curiosity and willingness to explore the captivating realm of argumentation! Take a break and have some fun by solving legal cases in the Survey while simulatenously helping science to progress.
